For a series RLC circuit, the differential equation is
If vT(t) is a constant or zero (
vT(t) = VT), and the system has initial conditions
![]() ,
and
,
and
![]() ,
then the solution to this
equation is
,
then the solution to this
equation is
| (RT C)2 - 4LC > 0 | (RT C)2 - 4LC = 0 | (RT C)2 - 4LC < 0 |
| Overdamped | Critically Damped | Underdamped |
|
|
|
|
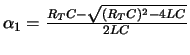 |
|
|
|
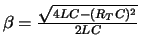 |
|
|
K1 = Vo - VT | K1 = Vo - VT |
|
|
|
For a parallel RLC circuit, the differential equation is
If iN(t) is a constant or zero (
iN(t) = IN), and the system
has initial conditions
![]() ,
and
,
and
![]() ,
then the solution to this equation is
,
then the solution to this equation is
| (GN L)2 - 4LC > 0 | (GN L)2 - 4LC = 0 | (GN L)2 - 4LC < 0 |
| Overdamped | Critically Damped | Underdamped |
|
|
|
|
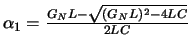 |
|
|
|
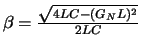 |
|
|
K1 = Io - IN | K1 = Io - IN |
|
|
|