%
% Filename: example5.m
%
% Description: m-file to compute and plot the truncated Fourier
% Series representation of a square wave.
%
% *** Plot truncatated FS for various numbers of terms. ***
clear; % clear matlab's memory
figure(1); clf; % open and clear figure 1
To = 2; wo = 2*pi/To; % fundamental period and frequency
D0 = 0.5; % signal offset
t = -2:0.01:4; % time over which we'll plot signal
N = [1 5 10 50]; % +/- values at which we'll truncate FS
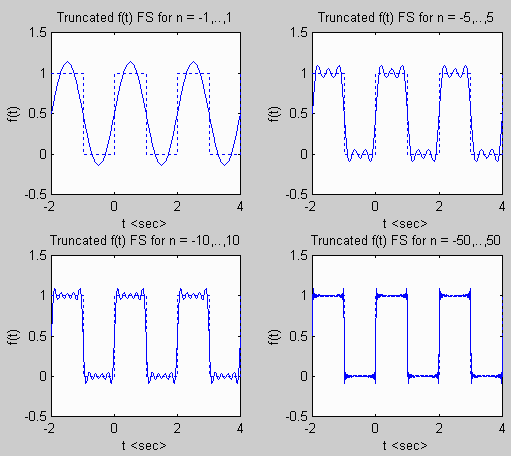
for i = 1:4, % compute truncated FS for above N values
f = D0*ones(size(t)); % start out with DC bias term
for n = -N(i):-1, % loop over negative n
Dn = (1 - exp(-j*n*pi))/(j*2*pi*n); % Fourier coefficient
f = f + real(Dn*exp(j*n*wo*t)); % add FS terms
end;
for n = 1:N(i), % loop over positive n
Dn = (1 - exp(-j*n*pi))/(j*2*pi*n); % Fourier coefficient
f = f + real(Dn*exp(j*n*wo*t)); % add FS terms
end;
subplot(2,2,i); % plot truncated FS representation of f(t)
plot(t,f); % and actual signal
hold on;
plot([-2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4],[1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1],':');
hold off;
xlabel('t ');
ylabel('f(t)');
titlevec = ['Truncated f(t) FS for n = ' num2str(-N(i)),',..,',num2str(N(i))];
title(titlevec);
end;
% *** Plot exponential magnitude and phase spectra for 1st 4 harmonics
clear; % clear matlab's memory
figure(2); clf; % open and clear figure 2
To = 2; wo = 2*pi/To; % fundamental period and frequency
D0 = 0.5; % signal offset, 0 frequency term
i = 1; % vector index to help store Dn and w
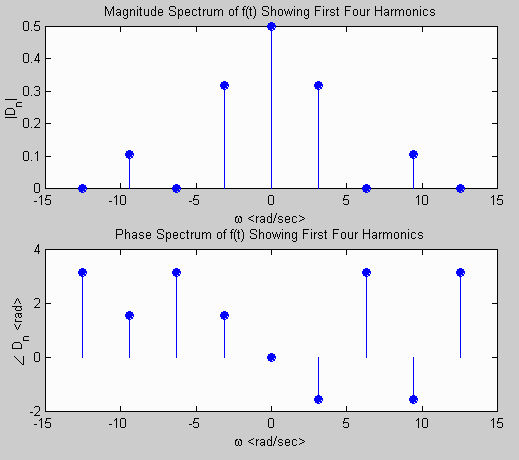
for n = -4:-1, % loop over negative n
Dn(i) = (1 - exp(-j*n*pi))/(j*2*pi*n); % Compute & store fourier coef.
w(i) = n*wo; % store associated frequency
i = i + 1; % increment vector index
end;
Dn(i) = D0; w(i) = 0; % store 0 frequency terms
i = i + 1; % increment vector index
for n = 1:4, % loop over positive n
Dn(i) = (1 - exp(-j*n*pi))/(j*2*pi*n); % Compute & store Fourier coef.
w(i) = n*wo; % store associated frequency
i = i + 1; % increment vector index;
end;
subplot(2,1,1); % plot magnitude spectrum of f(t)
stem(w,abs(Dn),'filled');
xlabel('\omega ');
ylabel('|D_n|');
title('Magnitude Spectrum of f(t) Showing First Four Harmonics');
subplot(2,1,2); % plot phase spectrum of f(t)
stem(w,angle(Dn),'filled');
xlabel('\omega ');
ylabel('\angle D_n ');
title('Phase Spectrum of f(t) Showing First Four Harmonics');
Matlab Plots Generated:

